Description
GoldBio’s EHA105 Agrobacterium chemically competent cells allow you to obtain high transformation efficiency in applications such as gDNA or cDNA library construction. Our EHA105 strain contains a rifampicin resistance gene (rif) and an amber basic Ti plasmid pEHA105 (pTiBo542DT-DNA) without self-transport function, containing the vir gene. EHA105 is ideal for genetic transformation of rice, tobacco and several other plants.
EHA105 chemically competent cells are free of animal-derived products and grown with animal-free media.
GoldBio’s EHA105 Agrobacteriumstrain was generated, and primary clone supplied by Dr. Elizabeth Hood.
Kit Components
Reagents Needed for One Reaction
- EHA105 Chemical Competent Agrobacterium: 50 µL
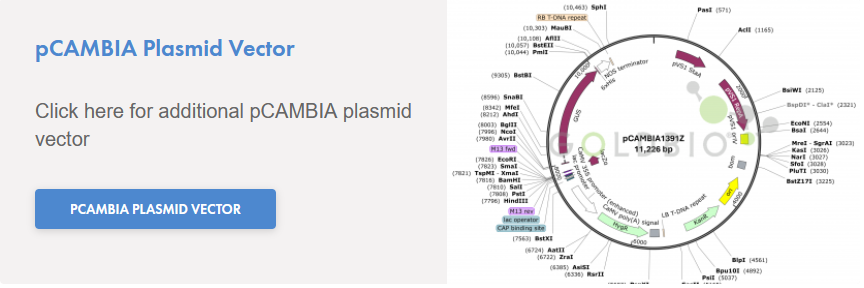
- DNA (pCAMBIA1391z Control, 10 ng/µL): 5 µL
- Recovery medium: 1 mL
Storage/Handling
This product may be shipped on dry ice. EHA105 Agrobacterium chemically competent cells should be stored at -80°C, pCAMBIA1391z Control DNA should be stored at -20°C and recovery medium should be stored at 4°C immediately upon arrival. When stored under the recommended conditions and handled correctly, these products should be stable for at least 1 year from the date of receipt.
Antibiotic Selection
Table 1: Antibiotic disc sensitivity for GoldBio’s Agrobacterium strains (using standard BD antibiotic discs)
| | Antibiotic Selection |
| Amp | Carb | Chlor | Gent | Kan | Rif | Spect | Strep | Tet |
| 100
µg/ml | 100
µg/ml | 30
µg/ml | 100
µg/ml | 30
µg/ml | 50
µg/ml | 25
µg/ml | 50
µg/ml | 50
µg/ml | 50
µg/ml |
| GV3101 | I | R | R | PR | R | S | R | S | R | S |
| EHA105 | R | R/S | R | n/a
| R/S | S | R | S
| R | S |
| LBA4404 | S | S | S | n/a | S | S | R | S | R | S |
| AGL-1 | R | R | R | n/a
| R/S | S | R | S | R | S |
| C58C1 | R | R | R | n/a | R/S | S | R | S | R | S |
| S = Sensitive
R = Resistant
R/S = intermediate zones using standard discs.
I = growth in inhibitory zone with standard disc. “Opaque”, not clear zone of inhibition. |
Quality Control
Transformation efficiency is tested by using the pCAMBIA1391z control DNA supplied with the kit and using the protocol given below. Transformation efficiency should be ≥5 x 104 CFU/µg pCAMBIA1391z DNA. Untransformed cells are tested for appropriate antibiotic sensitivity.
General Guidelines
- Handle competent cells gently as they are highly sensitive to changes in temperature or mechanical lysis caused by pipetting.
- Thaw competent cells on ice and transform cells immediately following thawing. After adding DNA, mix by tapping the tube gently. Do not mix cells by pipetting or vortexing.
Calculation of Transformation Efficiency
Transformation Efficiency (TE) is defined as the number of colony forming units (cfu) produced by transforming 1 µg of plasmid into a given volume of competent cells.
- TE = Colonies/µg/Dilution
- Colonies = the number of colonies counted
- µg = amount of DNA transformed in µg
- Dilution = total dilution of the DNA before plating
Example: Transform 1 µl of (10 pg/µl) control plasmid into 25 µl of cells, add 975 µl of Recovery Medium. Dilute 10 µl of this in 990 µl of Recovery Medium and plate 50 µl. Count the colonies on the plate the next day. If you count 250 colonies, the TE is calculated as follows:
Colonies = 250
µg of DNA = 0.00001
Dilution = 10/1000 x 50/1000 = 0.0005
TE = 250/0.00001/0.0005 = 5.0 × 1010